New ways to handle transaction related exceptions in mergers and acquisitions
Exceptions in the M&A process
Exceptions are present if
• Buyer or target or stakeholders change their expected behavior when transacting, transactions go wrong or do not generate the expected outcome
• Significant goals and objectives of tasks in the M&A process cannot be met or
• External effects hit (e. g. wars, embargoes, price hikes)
Such deviations from normal (expected) behavior are called exceptions. In this blog, we focus on exceptions of transactions.
Exceptions - why should i care?
You should care to avoid the „What you see is all there is“ trap
(D. Kahneman)
Which means can only see and handle situations that you have experienced, learned about, read or talked about.
Today, learning about exceptions is mainly driven by experience knowledge. Reason is: While there are many textbooks about M&A, very few talk about exceptions, even less about catastrophic exceptions like deal breakers and failures. That means if you are inexperienced you run the risks to run into exceptions without a plan. We should change that by providing knowledge about exceptions and by providing patterns of potential exceptions and how to address these.
transaction-related exceptions
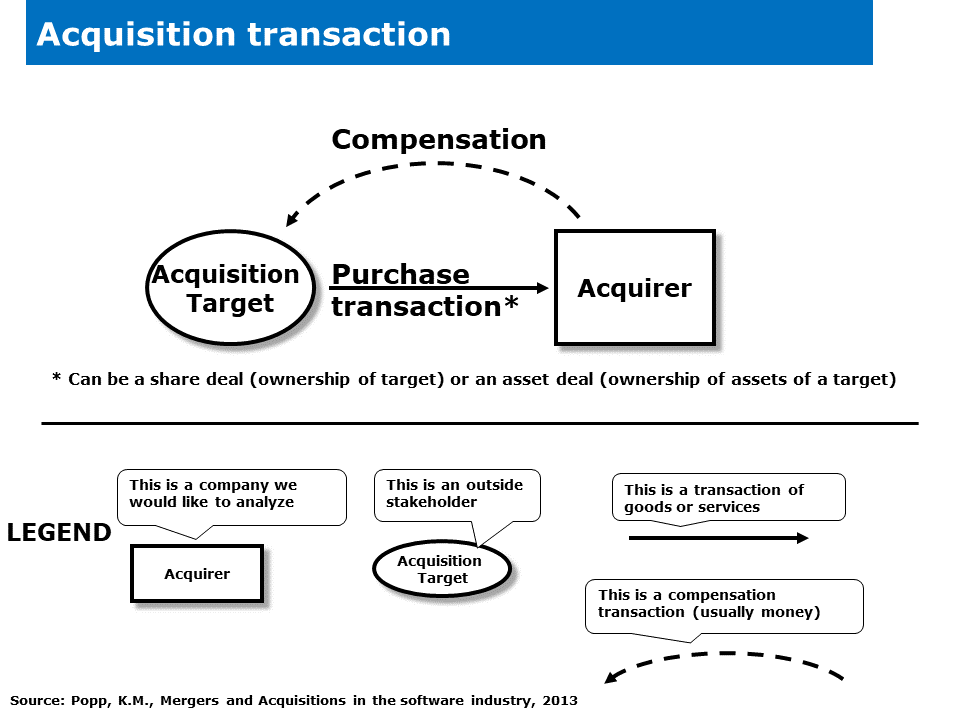
Let us see an acquisition transaction as a technical transaction.
The acquirer purchases all shares or some assets of the target and compensates this deal usually with money or other means of payment.
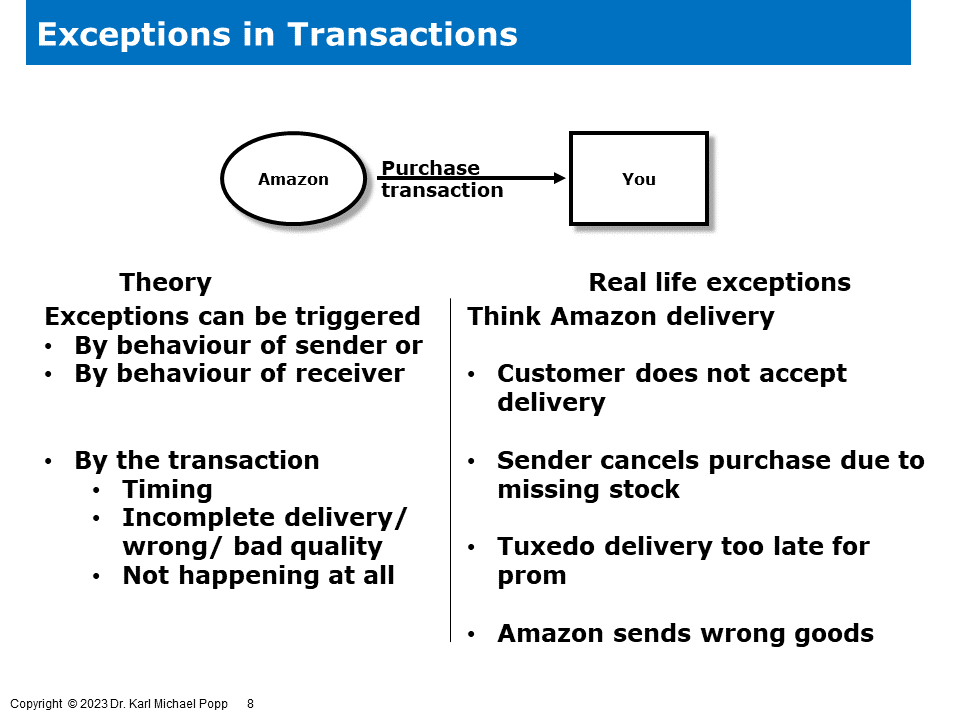
The theory of transactions tells us that there are potential risks associated with both the sender and the receiver of a transaction behaving strangely. When the sender exhibits strange behavior, it may result in the transmission of inaccurate or misleading information or goods, leading to misinterpretations or misunderstandings by the receiver. This can disrupt the effectiveness of the transaction process and hinder the successful completion of the transaction. On the other hand, if the receiver behaves strangely, they may fail to comprehend or respond appropriately to the sender's message, resulting in the breakdown of effective communication. These behavioral uncertainties can introduce errors, delays, or even complete failures in the transactional communication process, emphasizing the importance of individuals involved in a transaction maintaining clear, consistent, and rational behaviors.
So, how do you handle the transactions on the right hand side? The following picture provides ways to handle them.
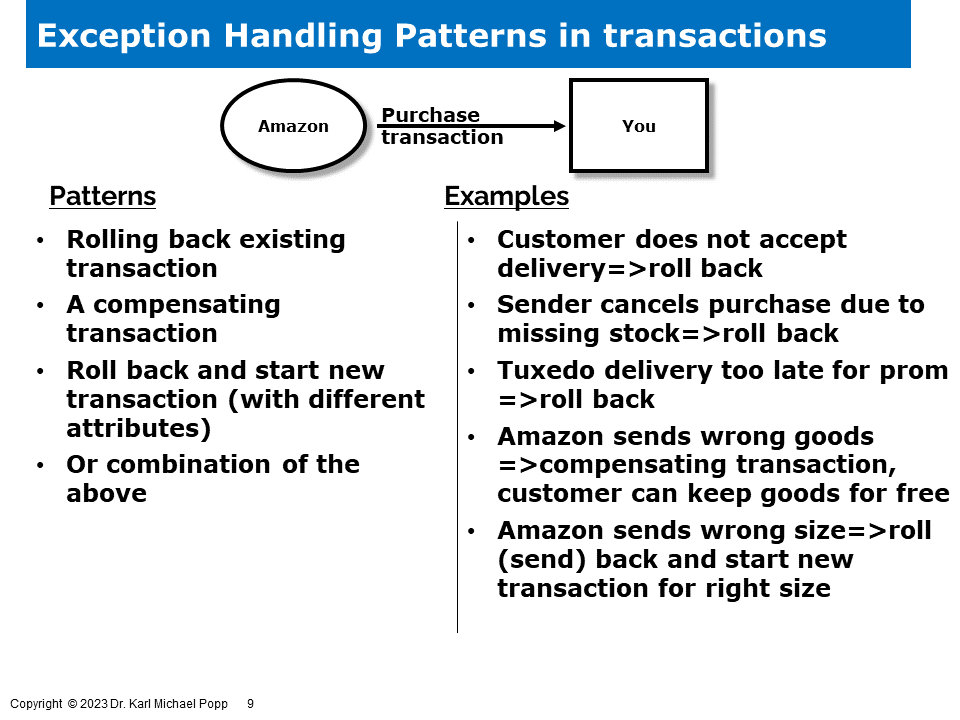
Rolling back and compensating transactions are powerful mechanisms that provide organizations with a safety net to rectify erroneous or fraudulent actions. By allowing the reversal of transactions, businesses can effectively undo any unintended or erroneous changes, restoring data integrity and eliminating any adverse impacts. On the other hand, compensating transactions come into play when a rollback is not feasible or practical. They help restore balance by executing a series of corrective actions that offset the negative consequences caused by a particular transaction, ensuring that the system remains consistent and reliable.
Looking at mergers and acquisitions, we see numerous exceptions in transactions. knowing about these and knowing about ways to handle these exceptions is paramount.